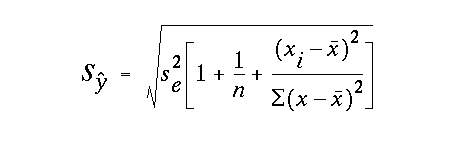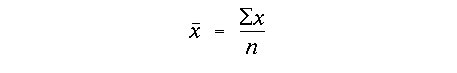
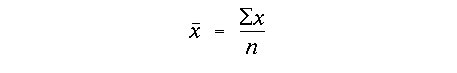
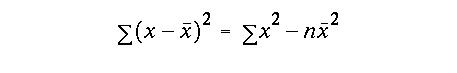
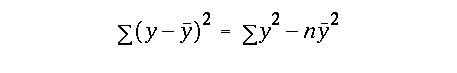
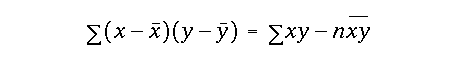
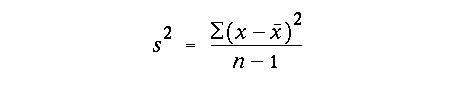
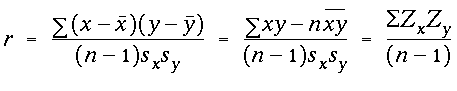
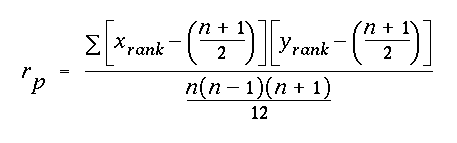
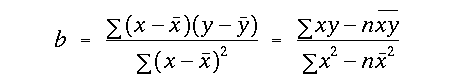
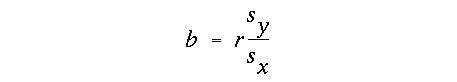
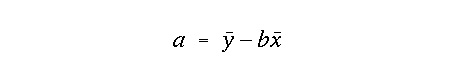
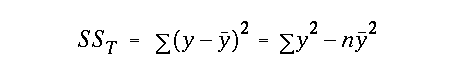
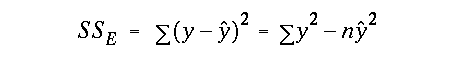
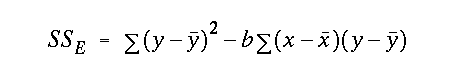
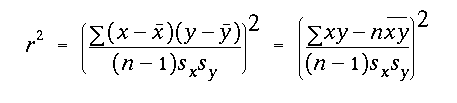
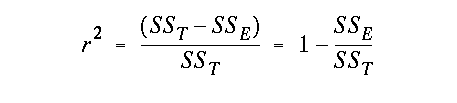
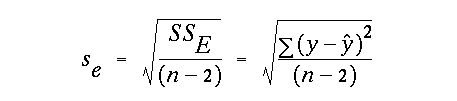
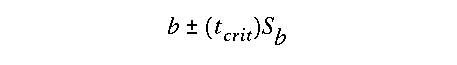
alpha value with df = (n - 2)and were
the standard deviation of the slope is defined as:
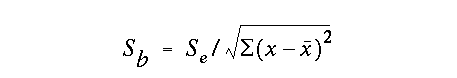
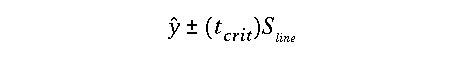
Note that t-crit is the critical t-value for a user selected
alpha value with df = (n - 2)and were
the standard deviation of the line is defined as:
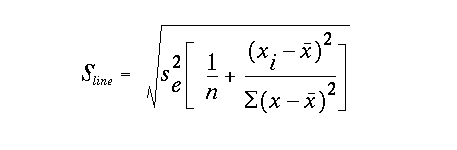
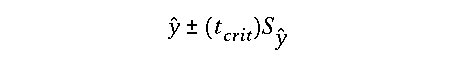
Note that t-crit is the critical t-value for a user selected
alpha value with df = (n - 2)and were
the standard deviation of the individual model prediction y-hat is defined as: